What is the Difference Between AA Alkaline Batteries and Other Battery Types
When it comes to powering our everyday devices, understanding the types of batteries available is crucial. Among them, AA alkaline batteries have emerged as a popular choice due to their long shelf life and reliable performance. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in energy storage solutions, “AA alkaline batteries strike a perfect balance between cost and efficiency, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.” This highlights the significance of evaluating the characteristics that set AA alkaline batteries apart from other battery types, such as lithium-ion and nickel-metal hydride.
The demand for AA alkaline batteries continues to grow as consumers seek dependable energy sources for everything from remote controls to digital cameras. However, the landscape of batteries is vast, with various types offering different advantages and disadvantages. By exploring the fundamental differences between AA alkaline batteries and other popular battery types, we can make more informed choices tailored to our specific needs. Understanding these distinctions not only enhances our appreciation of battery technology but also enables us to select the most suitable battery for our devices, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.

What are AA Alkaline Batteries?
AA alkaline batteries are one of the most commonly used types of batteries in household devices. They are cylindrical in shape with a diameter of about 14.5 mm and a height of approximately 50.5 mm. These batteries operate using a chemical reaction between zinc and manganese dioxide, which produces electrical energy. Due to their convenient size and widespread availability, AA alkaline batteries are often used in everyday items such as remote controls, flashlights, and toys.
One of the key features of AA alkaline batteries is their ability to provide a steady voltage output, typically 1.5 volts, making them suitable for both low and moderate drain devices. Their energy capacity generally allows for a longer usage time compared to other battery types, such as zinc-carbon batteries. Additionally, AA alkaline batteries have a relatively low self-discharge rate, meaning they can retain their charge for many months if not used. This quality, along with their affordability, contributes to their popularity as a reliable power source for a variety of electronic devices.
Comparison of AA Alkaline Batteries with AA Lithium Batteries
When comparing AA alkaline batteries and AA lithium batteries, several key differences come to light. AA alkaline batteries are typically the go-to choice for low-drain devices. They work well in gadgets like remote controls, clocks, and toys, providing steady voltage and performance at an economical price. However, they tend to have a shorter lifespan and may struggle under heavy load conditions, leading to reduced efficiency in high-drain devices such as digital cameras or gaming controllers.
On the other hand, AA lithium batteries excel in high-drain applications. They offer a much higher energy density, which means they can power devices for a longer duration without needing a replacement. Additionally, lithium batteries have a wider temperature operating range and can perform better in extreme conditions, making them ideal for devices used in outdoor environments. Although they are typically more expensive than alkaline batteries, their longevity and reliability in demanding situations make them a preferred choice for users seeking optimum performance.
Comparison of AA Alkaline Batteries and AA Lithium Batteries
Performance Characteristics of AA Alkaline Batteries vs. Rechargeable NiMH Batteries
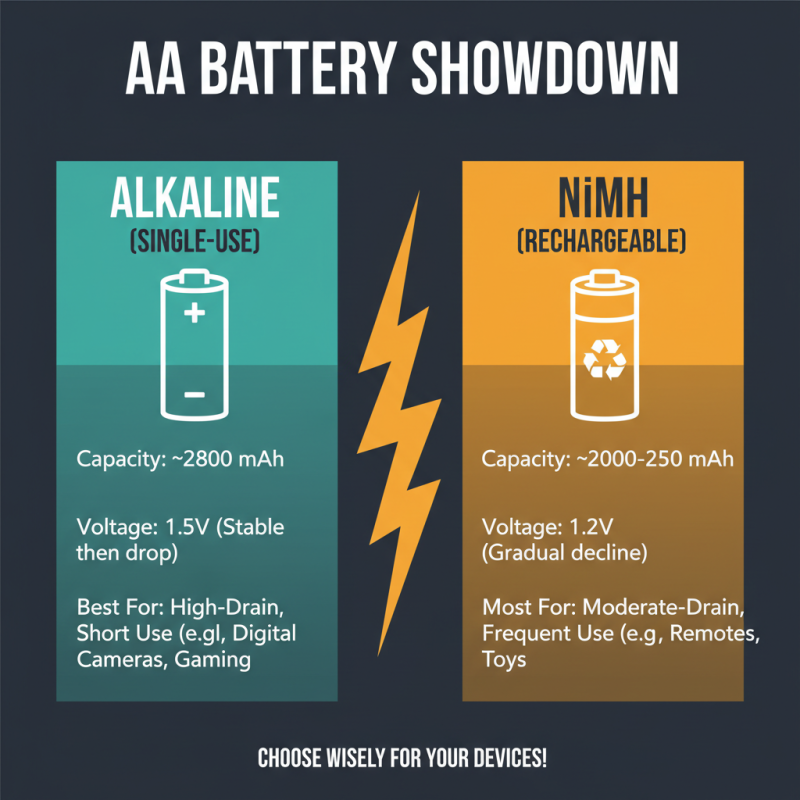
AA alkaline batteries and rechargeable nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries differ significantly in their performance characteristics, making them suitable for various applications. Alkaline batteries typically have a higher energy density, providing around 2,800 mAh capacity. This makes them an excellent choice for devices with high power consumption for short durations, such as digital cameras or handheld gaming devices. Their voltage output of 1.5 volts tends to remain stable until the battery is nearly depleted, allowing for reliable performance in many consumer electronics.
In contrast, NiMH batteries offer advantages in long-term use, particularly with devices that require frequent battery replacement. With a nominal capacity of about 2,000 to 2,400 mAh, they can be recharged hundreds of times, contributing to reduced waste and cost-effectiveness over time. NiMH batteries also exhibit lower self-discharge rates compared to alkaline batteries, retaining about 80% of their charge after one month of inactivity. According to a report from the Battery University, the cycle life of rechargeable batteries like NiMH can reach up to 1,000 cycles, making them a sustainable choice for high-usage applications such as remote controls, wireless mice, and other gadgets.
When evaluating these battery types, factors such as environmental impact and cost should also be considered. While the initial cost of alkaline batteries may be lower, the total cost of ownership over an extended period favors rechargeable NiMH batteries for regular use. Ultimately, understanding these performance characteristics helps consumers choose the most effective power source for their specific needs.
Applications of AA Alkaline Batteries in Everyday Devices
AA alkaline batteries are prevalent in countless everyday devices, showcasing their versatility and efficiency.
With a voltage of 1.5V and a capacity ranging from 1800 to 3000 mAh, these batteries are ideal for high-drain devices such as digital cameras, remote controls, and handheld gaming systems.
According to industry reports, the alkaline battery market is expected to grow steadily, reaching a valuation of approximately $8 billion by 2027, driven by the relentless demand for portable power sources.
Tips: When using AA alkaline batteries in high-drain devices, consider investing in devices that can optimize battery life, such as energy-efficient gadgets. This not only enhances performance but also prolongs the operational lifespan of your batteries.
Moreover, AA alkaline batteries are also commonly found in low-drain devices like clocks, flashlights, and toys.
Their ability to deliver steady power over a longer period is essential for devices that do not require constant energy bursts.
Studies indicate that alkaline batteries can retain a significant percentage of their capacity even after years of storage, making them a reliable choice for long-term use.
Tips: Always check the expiration date on your AA alkaline batteries before use. Storing them in a cool, dry place can substantially extend their shelf life and ensure optimal performance when needed.
Cost and Environmental Considerations of AA Alkaline Batteries vs. Other Types

When comparing AA alkaline batteries to other battery types, cost and environmental considerations play a crucial role in consumer decision-making. AA alkaline batteries are typically more affordable than rechargeable alternatives like NiMH (nickel-metal hydride) or lithium-ion batteries. According to industry reports, a pack of AA alkaline batteries can cost around $5 to $10, while a rechargeable NiMH pack may range from $15 to $30. This initial price difference makes alkaline batteries attractive for consumers who require batteries for low-drain devices such as remote controls and wall clocks, where the cost-effectiveness of single-use batteries prevails.
However, the environmental impact of these batteries cannot be overlooked. It is estimated that approximately 15 billion alkaline batteries are sold annually in the U.S. alone, contributing significantly to landfill waste. In contrast, NiMH batteries can be recharged up to 500 times, leading to a substantially lower lifetime cost and environmental footprint when used in high-drain devices. The National Recycling Coalition reports that recycling rechargeable batteries can recover up to 95% of their materials, reducing pollution and resource extraction associated with new battery production. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the long-term benefits of rechargeable batteries may outweigh the initial cost savings of traditional AA alkaline batteries, influencing their purchasing decisions.
Related Posts
-

The Science Behind AA Alkaline Batteries and Their Environmental Impact
-

Common Issues Faced by Global Buyers When Sourcing Procell AA Batteries
-

7 Compelling Reasons to Choose the Best CIC Rechargeable Hearing Aids for Your Hearing Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Hearing Aid Batteries for Optimal Performance and Longevity
-

How to Choose the Right AA Batteries for Your Devices: Essential Tips
-

Exploring Alternative Energy Solutions: The Rise of Procell AA Batteries in Global Markets
